Comparación de métodos de diagnóstico para el tratamiento hemodinámico en recién nacidos y prematuros utilizando la medición de la vena cava, lactato y criterios clínicos Artículo Original
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
Introducción: No existe un criterio único para evaluar el estado hemodinámico de los recién nacidos y prematuros y las diferentes variables en el grupo de recién nacidos, como la edad gestacional, el peso al nacer y los períodos de nacimiento.
Métodos: Se trata de un estudio observacional descriptivo, transversal, epidemiológico con dos cohortes de pacientes. Los recién nacidos a término y Pretérmino, atendidos en la Unidad de Neonatal del Hospital Pablo Arturo Suárez, participan durante los meses comprendidos entre abril y septiembre de 2019.
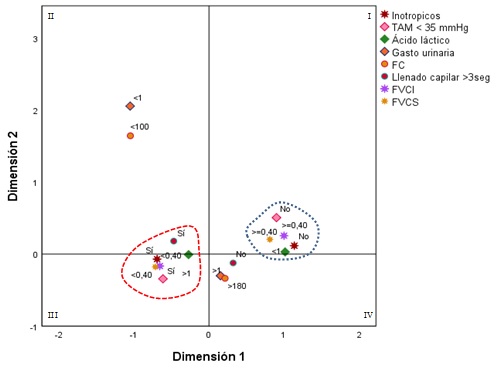
Resultados: la medición ecográfica del flujo de la vena cava (FVC) es útil para el tratamiento de manejo del paciente neonatal hemodinámicamente inestable. La muestra estuvo conformada por 110 recién nacidos atendidos en el servicio de neonatología del Hospital Pablo Arturo Suárez desde noviembre de 2019 a enero de 2020. Quito, Pichincha, Ecuador. Las variables bajo peso al nacer y prematuridad moderada tienen un valor estadísticamente significativo para el uso de inotrópicos. Las demás variables no presentan valor estadísticamente significativo. La frecuencia cardíaca, el gasto urinario, la presión arterial media, el ácido láctico, el llenado capilar, el flujo de la vena cava superior y el flujo de la vena cava inferior tienen valores estadísticamente significativos. Las comparaciones de FVCI y FVCS con frecuencia cardíaca, gasto urinario, presión arterial media, ácido láctico, llenado capilar tienen un valor estadísticamente significativo, excepto para el llenado capilar> 3 segundos en FCVI. Se utilizó el análisis multivariado de Componentes Principales Categóricos (CATPCA) para caracterizar el estado hemodinámico e inotrópico, que resultaron significativos en el análisis bivariado. Dimension, uno de los gráficos bidimensionales, discrimina el uso o no de inotrópicos y las categorías de parámetros hemodinámicos TAM <35 mmHg, ácido láctico, llenado capilar, FVCI y FVCS. La dimensión dos discrimina entre las categorías de gasto urinario y FC.
Conclusión: En recién nacidos a término y prematuros con bajo peso y adecuado peso al nacer con inestabilidad hemodinámica en general, que fueron evaluados con ecografía para medir el flujo de la vena cava, la concordancia entre los criterios clínicos y la valoración ecográfica del flujo fue de 0,4 cm / seg en ambos métodos. Esta situación significa que la medición de los flujos cava venosos por ecografía es útil para evaluar el estado hemodinámico de los pacientes neonatales.
Descargas
Detalles del artículo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.