Higher concordance in clinical assessment versus ultrasound to estimate fetal weight when compared with birth weight in full-term newborns Original Research
Main Article Content
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this trial was to estimate fetal weight by clinical and ultrasound methods and to compare it with the weight at birth in full-term newborns.
Methods: This is an epidemiological, observational, cross-sectional study of a cohort of healthy full-term newborns. The sample size was 102 neonates born at the Pablo Arturo Suarez Hospital, in Quito, Ecuador, from November 2019 to January 2020.
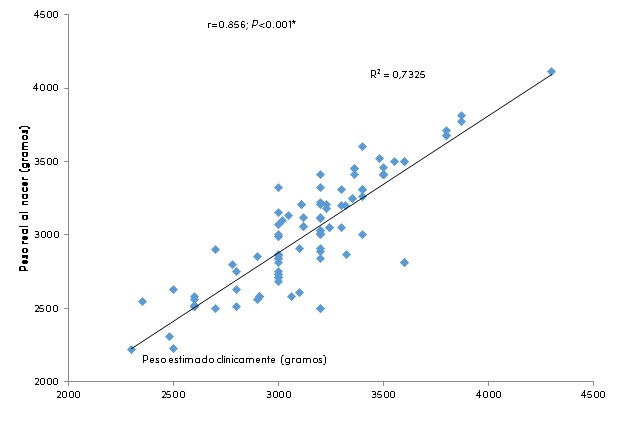
Results: In full-term neonates, the estimate on ultrasound was 80.00%, while in the clinical assessment, it was 72.29%. The newborns analyzed were male, mestizo, Ecuadorian, and born in the highlands region with a mean gestational age of 38.67 weeks and a mean birth weight of 3,023 grams. We estimated the fetal weight through ultrasound and clinical assessment. The estimation of the absolute error in both methods analyzed was 2.43% in ultrasound and -4.65% in clinical assessment, and both showed moderate concordance: 78.2% in ultrasound and 85.6% in clinical assessment. Multivariate analysis showed the neonates with modified weight by ultrasound are 13.44 times more likely to show altered weight at birth, while neonates with modified weight by the clinical assessment are 11.95 times more likely to show altered weight at birth.
Conclusions: Accuracy in the clinical assessment was always higher than in the ultrasound method, especially in low-weight newborns.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

 ORCID:
ORCID: