Chagas disease in a child living in an urban area at 2850 meters above sea level Case Report
Main Article Content
Abstract
Introduction: Chagas disease is a parasitic disease transmitted by vectors with echo-epidemiological characteristics caused by the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi. From 2013 to 2019, Ecuador reported 108 acute cases, of which 7 were in the province of Pichincha. We present the case due to its ecoepidemiological characteristics.
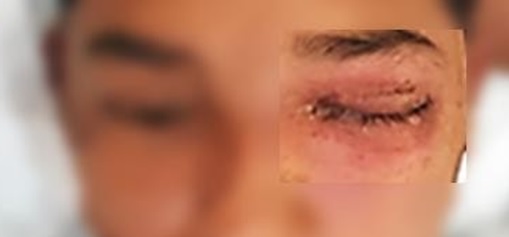
Clinical case: An acute case of a 14-year-old male resident in a nonendemic area that began with Romaña's sign, fever of three weeks of evolution with mild splenomegaly and concentric hypertrophy of the left ventricle.
Evolution: The patient was treated with benznidazole 7 mg/kg/day orally every 8 hours for two months, support measures and multidisciplinary follow-up.
Conclusion: The detection zone was the northeast of the metropolitan district of Quito, which is part of health district 17D01, without previous reports until 2016, whose appearance could be related to changes in the local ecosystem and the impact on the transmission of vector diseases.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.